Abstract
Background: Heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a rare immune mediated complication that is triggered in a subset of patients temporal to therapeutic heparin exposure. Laboratory testing is based on screening for the presence of serum anti-PF4 antibodies using sensitive solid-phase immunoassays. If antibodies are detected, functional testing to demonstrate the platelet activating properties and heparin dependence of these immune complexes is then performed. Previous studies have reported possible clinical utility in identifying non heparin dependent platelet activating antibodies using a buffer control with zero heparin in the serotonin release functional assay (SRA). These reports suggested a correlation between reactivity in the zero heparin buffer control and pathogenicity of HIT antibodies which may define a subtype of HIT, referred to as autoimmune HIT. We aimed to investigate the utility of zero heparin buffer control as a part of an inhouse validation study of a mass spectrometry-coupled SRA (Mayo-SRA).
Methods: Three hundred archived serum samples were tested using anti-PF4 IgG antibody enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA; Immucor Diagnostics, GA, USA). SRA was preformed on all samples using Mayo-SRA and reference 14C SRA methods. Zero heparin control buffer was included in the Mayo-SRA assay. Serotonin release >20% in the low dose heparin (0.1U/mL, LDH) and ELISA optical density (OD) >0.4 were considered positive. Drug interference studies were performed by spiking known SRA-positive samples with increasing concentrations of unfractionated heparin (UFH), low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) or fondaparinux in the LDH and zero heparin SRA. The clinical 4T score was calculated retrospectively calculated for all patients.
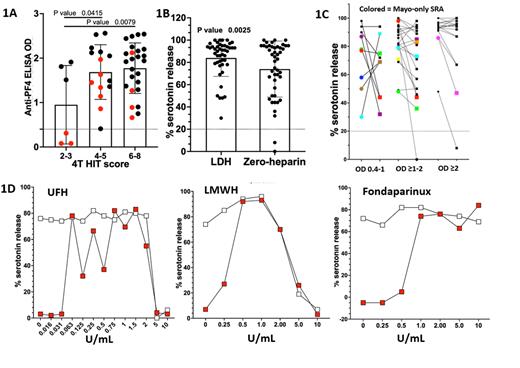
Results: Of the 300 tested samples, 57 were anti-PF4 ELISA positive. 33 of the 57 samples were positive using the reference 14C SRA method. Whereas 43 samples were positive by Mayo-SRA assay. Three additional samples were positive by Mayo-SRA, but negative by both screening anti-PF4 ELISA and the reference SRA method (Fig- 1A). Lastly, 13 samples were anti-PF4 ELISA positive, but SRA negative by both methods in comparison. Interestingly, 44 of 46 (95%) samples interpreted positive by LDH were also interpreted positive (serotonin release >20%) under zero heparin conditions. These included the 3 samples that were positive by Mayo-SRA but negative by both screening anti-PF4 ELISA and the reference SRA. The overall % serotonin release using zero heparin control was significantly lower (P= 0.003, paired Student T-test) compared to LDH (Fig-1B). In addition, zero heparin followed a similar pattern as LDH, with highest levels at ELISA OD units >2 (Fig-1C).
Strikingly, drug interference studies showed artifactual serotonin release in the zero heparin reaction, which was not detected in the absence of spiked drugs. For UFH, serotonin release in zero heparin control occurred at very low spiked concentrations, ≥0.063 U/mL. LMWH and fondaparinux spiking experiments also displayed similar zero heparin serotonin release patterns (Fig-1D). Of note, none of these interferences were detected in UFH spiked SRA-negative samples (data not shown).
Conclusion: Contrary to prior results suggesting that less than 50% of LDH SRA positive samples are also positive in the zero heparin SRA, our results show high zero heparin SRA positivity rate of >95%. Zero heparin SRA showed a pattern with highest levels at ELISA OD units >2 suggesting that reactivity in this condition is a function of antibody strength rather than a qualitative difference (i.e. "autoimmune" HIT antibodies vs "non-autoimmune" HIT antibodies). In addition, contamination of patient sera with small amounts of remnant heparin can significantly impact platelet activation in the zero heparin SRA test. Thus, zero heparin SRA positive results may be artifactual and represent residual heparin contained in the patient sample.
Figure legend:
Fig-1A. Scatter plots of SRA positive samples grouped by 4T scores. Red dots are Mayo-SRA only positive samples. Fig-1B and Fig-1C. Scatter plots of % serotonin release of Mayo-SRA positive samples at LDH (circles) vs. zero heparin buffers (squares), and grouped by ELISA OD values, respectively. Fig-1D. % Serotonin release of known SRA-positive samples spiked with increasing concentrations of UFH, LMWH, or fondaparinux at LDH (white) or zero heparin buffers (red).
Pruthi: CSL Behring: Honoraria; Genentech: Honoraria; Bayer Healthcare AG: Honoraria; HEMA Biologics: Honoraria; Instrumentation Laboratory: Honoraria; Merck: Honoraria. Padmanabhan: Veralox Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal